Although females make up fewer than half of all civilian workers, they comprise more than 75 percent of workers in the health sector (figure 10.4a). This share varies dramatically across different components of the health industry. In the goods-producing part of the industry—manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, and supplies (which together make up only 6.5 percent of health sector employment)— the female share is slightly less than among all civilian workers.
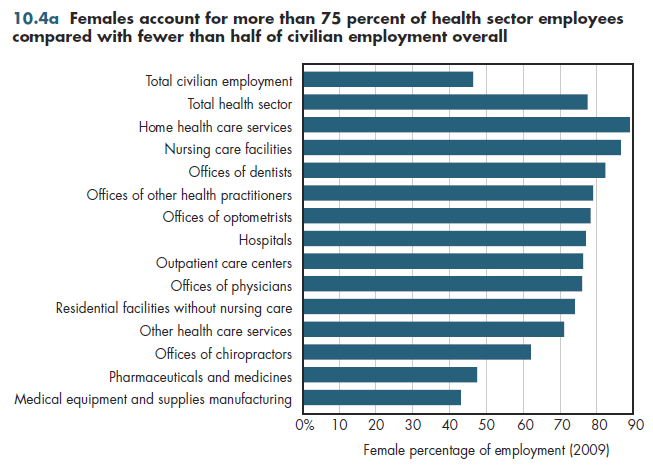
In the services part of health care, the share of female workers is dramatically higher. In home health care, nine of 10 workers are women. In nursing-care facilities, seven of eight workers are female (although in residential facilities that do not provide skilled nursing care, the female share is less than 75 percent). Most ambulatory health services have a workforce in which women make up 75 percent of employees. Hospital workers have approximately the same share of female workers.
The differences in share of females are even wider at the individual occupational level. Women make up 88 percent of health care support occupations such as nursing and home health aides, compared with fewer than 75 percent of workers in health care practitioner and technical occupations. In the five health-related occupations that have the highest share of females, women make up more than 90 percent of employees (figure 10.4b). Also shown are registered nurses (RNs), who make up the single largest occupation in health care, almost 90 percent of whom are female.
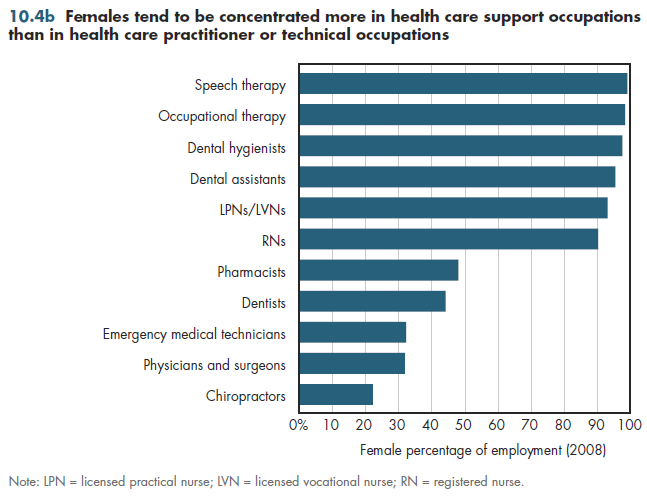
The five occupations in which women are least represented include four that require doctoral training; these include chiropractors (22 percent), physicians and surgeons (32 percent), dentists (44 percent), and pharmacists (48 percent). Although some pharmacists have only bachelor's degrees, all newly minted pharmacists now must have a doctorate. However, these numbers are gradually changing. Currently, females comprise half of all medical students; chiropractics is also seeing an increase in the female share of graduates.
Download PowerPoint versions of both figures.
Download Excel workbooks used to create
Figure 10.4a Table and
Figure 10.4b Table.
[Note that you’d have separate links for each set of tables] Figures 10.4a and 10.4b were created from the following tables
(the workbook includes all supporting tables used to create these tables):
- Fig. 10.4a: Table 10.4.1 Female Percentage of All Employees by Health Sub-Sector and Total Civilian Employment, 2007, 2009 and 2010
- Fig. 10.4b: Table 10.4.2. Female Percentage of All Employees by Health Sub-Sector and Total Civilian Employment, 2008
- Author's calculations.
- Department of Labor. Bureau of Labor Statistics.